@Jo-CKC-Studio yes that’s exactly it. We used to worry that our kids did not see each other face to face. They just texted or snap-chatted or whatever. Now we have to wonder if there is even a human being on the other end.
@Jo-CKC-Studio Your comments are reminding me of the recent movie M3GAN, which contained a few thought-provoking moments on the potential dangers of children bonding with AI.
James Cameron makes an interesting parallel between AI and Plato’s famous “Allegory of the Cave” in which people are chained within a cave and only see shadows on the wall. It is the only reality they know, so they accept the shadows as “real”.
Socrates went on to comment on this allegory, saying (roughly) that a philosopher is one who understands that they are only seeing shadows on the wall, and that an entire other reality exists.
Interesting – thanks for sharing @MorseBranded1. To me, when I think of The Cave in relation to AI, I also think about whether AI systems could have limitations in their understanding of the world similar to the people in the cave. It’s not just us humans that are potentially limited in this situation.
Japan is working on creating its own versions of ChatGPT, the popular AI chatbot developed by OpenAI. The Japanese government and major tech companies like NEC, Fujitsu, and SoftBank are investing heavily to develop AI systems based on large language models (LLMs) that can understand and interact in the Japanese language. The challenge arises from the fact that existing LLMs, like GPT-3, are primarily trained in English and may struggle with Japanese due to differences in sentence structure, limited data, and cultural nuances. Japanese researchers are concerned that AI systems trained on foreign language data cannot fully grasp the intricacies of the Japanese language and culture.
The goal is to create Japanese LLMs that not only understand the language but also reflect cultural practices accurately. Researchers are ranking the performance of these models using tools like Rakuda, with the hope that Japanese LLMs will eventually catch up with or surpass their English counterparts. Efforts are underway to create a Japanese LLM using the Fugaku supercomputer, which is expected to be released next year. The Japanese Ministry of Education is also funding the development of a Japanese AI program for scientific research, which is set to be publicly released in 2031.
Additionally, Japanese companies like NEC and SoftBank are already commercializing their own LLM technologies for various industries, including finance, transportation, logistics, and research institutions. Researchers believe that a precise, made-in-Japan AI chatbot could accelerate scientific research and foster international collaborations.
Question for readers: What are your thoughts on Japan’s efforts to develop its own AI chatbot and language models? Do you think specialized language models for different languages and cultures are important for the future of AI communication? #AI #LanguageModels #ChatGPT #TechnologyTrends
It totally makes sense for Japan to develop their own AI systems that aren’t just translations of English models, but are engineered from the ground up for the Japanese context.
Language is intricately tied to culture, (norms, histories, and values differ widely across regions), so creating LLMs that understand the nuances of Japanese (or that of any language) requires training models on native Japanese data and accounting for sociolinguistic norms. It is certainly much different from an English-language trained LLM that then translates into another language (which is currently what is available globally). Also, languages have fundamental differences across vocabulary, grammar, syntax, and phonetics that make training a single LLM across languages difficult.
And then there’s consideration of regulations, privacy and ethics, which all vary depending on region, (and was evident with the Italian governments reaction to the release of ChatGPT; to ban its use due to privacy concerns). Ultimately each language and region needs models specifically engineered for its own language, culture and regulatory environment, rather than any one-size-fits-all solution.
So yes, I absolutely believe that specialised language models for individual countries are certainly important for inclusivity and accessibility to these new tools of productivity on a global scale.
![]()
![]() AI’s Dominance in Crypto Trading: A Game-Changer!
AI’s Dominance in Crypto Trading: A Game-Changer! ![]()
![]()
In the fast-paced world of cryptocurrency trading, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is taking center stage, revolutionizing how we navigate this volatile landscape. Here are the key takeaways from a recent article:
1. AI Rules the Markets: In traditional stock markets, algorithmic trading dominates, with high-frequency trading, bots, and AI-driven strategies accounting for 60-75% of all trades. AI, particularly Machine Learning (ML), plays a pivotal role in enhancing these trading strategies.
2. AI Goes Retail: AI’s power is no longer confined to Wall Street. Retail traders now have access to AI-driven tools, especially in the crypto space. Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT help traders analyze charts, trends, and indicators, providing insights into market dynamics and investment opportunities.
3. Real-World Applications: Several platforms, including Coinbase, are using AI like ChatGPT for risk analysis. Crypto bots like Omni support passive income strategies, while SingularityNET offers AI bots for market analysis.
4. Predicting Volatility: AI is being employed to forecast the wild swings in cryptocurrency prices. For instance, GNY.io’s machine learning tool uses advanced algorithms and models to analyze price patterns and generate trading signals. It boasts an impressive accuracy rate of over 95%.
5. Taming Emotions: Emotions can be a trader’s worst enemy. AI-powered trading bots are immune to fear and greed, executing predefined strategies without emotional bias.
6. Caveats to Consider: While AI holds immense potential, there are caveats. AI programs like ChatGPT are still in beta and may not always predict market behavior accurately. Data security and privacy concerns also loom.
7. A Collaborative Future: AI won’t replace human traders; it will complement their abilities. Collaborations between humans and machines are key to achieving the best trading outcomes.
8. Regulation on the Horizon: The AI industry is undergoing discussions on regulation. This includes debates on “open” vs. “closed” AI development. In the financial sector, AI is just getting started, and retail crypto traders stand to benefit.
AI is reshaping the crypto trading landscape, offering powerful tools to both professionals and retail traders. As the industry evolves and AI regulations take shape, expect more exciting developments in the world of cryptocurrency trading! ![]()
![]()
![]() #CryptoTrading #AIRevolution
#CryptoTrading #AIRevolution
@MFrank - I find AI super useful as a research tool for various assets. Basically it makes it possible for someone with limited time to do some deep diving into specific projects. So yes - as per @Nancy_Muellerhof’s post:
“2. AI Goes Retail: AI’s power is no longer confined to Wall Street. Retail traders now have access to AI-driven tools, especially in the crypto space. Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT help traders analyze charts, trends, and indicators, providing insights into market dynamics and investment opportunities.”
You can use ChatGPT Pro with a subscription to upload csv spreadsheets to create and analyze charts. But for a free, AI research tool, Perplexity is great. It can access the internet, so you can ask it to simplify complex articles, helping you understand the technologies behind various projects. Importantly, it provides data sources for all answers, so you can cross-check the information.
Breakthrough in Intelligence Services’ AI Raises Urgent Call for Private Industry to Safeguard Privacy
In recent groundbreaking developments, the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) has unveiled a ChatGPT-style AI designed to revolutionize intelligence operations within the United States. However, this extraordinary leap in AI technology shines a glaring spotlight on the critical need for the private industry to actively engage in the protection of individual privacy.
AI’s Transformation of Data into Information: This new CIA AI represents a monumental shift in the intelligence community’s capabilities. It empowers analysts to convert colossal volumes of raw data into actionable information swiftly. Here, it’s crucial to differentiate between raw data and information: Raw data is the unprocessed, often meaningless input, while information is the structured, meaningful output that informs decisions.
The Snowden Revelation and Its Implications: Reflecting on the past, we remember the revelations made by NSA whistleblower Edward Snowden, exposing the massive scale of surveillance on U.S. citizens with official authorization. Until now, the vast troves of collected data were relatively safe from being weaponized for political gain or people control due to the sheer volume making it unwieldy to process.
The Race for Technological Supremacy: However, this latest AI advancement underscores the relentless pace of technological evolution. Intelligence agencies, driven by the imperative to stay ahead of global counterparts, continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible. An ethical ban on such technologies in one country wouldn’t deter their development elsewhere, leaving us at a disadvantage.
Private Industry’s Crucial Role: The solution lies in private industry’s active involvement in AI, particularly in safeguarding privacy. The headline-worthy idea is clear: “The Deployment of Intelligence Services’ AI Breakthrough Highlights the Urgent Need for Private Industry to Develop AI that Protects Privacy from Information Gathering.”
In this rapidly changing landscape, private industry must take the lead in creating AI systems and technologies that prioritize individual privacy. Collaborations between tech experts, ethicists, and policymakers can strike the right balance between innovation and safeguarding our fundamental rights.
The future of AI hinges on whether we can harness its immense potential while upholding ethical principles and protecting the privacy and freedoms of individuals. It’s a challenge we must face head-on, together.
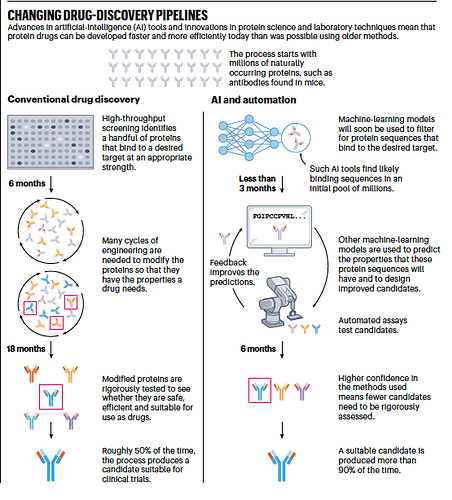
Some background:
Protein drugs offer unique advantages due to their size and surface area, allowing for more interactions with target molecules. However, developing these drugs is notoriously difficult, with a success rate of less than 10% in clinical trials.
AI can aid the development process by gathering extensive data on previous candidates, as well as improving computer models that predict drug behavior in the body.
Additionally, collaborative efforts, like federated learning, can pool resources without revealing competitive data; and active learning can fine-tune data generation for better model predictions. This enables collaboration among competitive companies that can accelerate protein drug development and improve success rates.
Source: Nature
Thanks for posting this. It raises an interesting question of how competing companies can collaborate on training AI for mutual benefit, without disclosing trade secrets to one another. Here are a few ways this can be accomplished:
- Trusted Third-Party Intermediaries:
- Employ a trusted third-party intermediary, such as a neutral research institution or consultancy, to facilitate collaboration. These intermediaries can mediate data sharing and analysis without exposing sensitive information.
- Federated Learning:
- A technique that allows multiple parties to collaboratively train a machine learning model without sharing raw data. Each company trains its model on its data and then shares only model updates or aggregated information with other parties.
- Homomorphic Encryption:
- Performs computations on encrypted data. With this technique, data can be kept encrypted while still allowing joint analysis and computation without disclosing the underlying data.
- Secure Multiparty Computation (SMPC):
- Enables multiple parties to jointly compute a function over their private inputs without revealing those inputs. SMPC ensures that each party keeps its data secret while collaborating.
- Data Anonymization and Masking:
- Anonymize or mask sensitive data before sharing it with collaborators. This involves removing or obfuscating personally identifiable information (PII) and trade secrets, allowing for safer data sharing.
- Differential Privacy:
- Techniques to add noise to aggregated statistics and analysis results, ensuring that individual data points cannot be reconstructed or reverse-engineered from the collaborative outputs.
- Use Case-Specific Data Sharing Agreements:
- Clear and legally binding data sharing agreements that define what can and cannot be shared. These agreements should specify the scope of collaboration and data handling practices.
- Secure Collaboration Platforms:
- Secure, encrypted collaboration platforms and tools designed for data sharing and analysis among multiple parties. These platforms should have robust access controls and audit logs.
- Redundant Data Removal:
- Protocols that remove any redundant or unnecessary data after the collaboration is complete to minimize the risk of data exposure.
- Independent Model Verification:
- Methods for independently verifying the results or models produced through collaboration without exposing the underlying data. This can involve auditing the model or verifying its outputs using trusted algorithms.
- Non-Disclosure Agreements (NDAs):
- Legally bind collaborating parties to keep shared information confidential.
- Limit Scope and Duration:
- Restrict the scope and duration of collaboration to minimize the exposure of sensitive information. Only share what is essential for achieving the collaborative goals.
Some of these AI girlfriends aren’t bad
Apropos of this general AI discussion: except from a great presentation by @Delia-CKC-Fund
Both blockchain and AI are disrupting the financial industry and changing the landscape. ![]() AI can process data faster than humans and allows financial institutions to extract more insights and automate repetitive tasks.
AI can process data faster than humans and allows financial institutions to extract more insights and automate repetitive tasks. ![]()
Blockchain is also disrupting the industry by providing more transparency and access to financial markets through decentralized finance (DeFi) and smart contracts. ![]() The launch of more decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) – and the ways that these interface with AI – will force us to rethink the existing centralized financial systems.
The launch of more decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) – and the ways that these interface with AI – will force us to rethink the existing centralized financial systems. ![]()
![]() #FinTech #AI #Blockchain #defi
#FinTech #AI #Blockchain #defi
@SolarTwin Relatedly, in terms of forming relationships with AI, interesting to consider the recent M3GAN comedy-horror in light of existing toys like CODI that have similar (albeit less advanced) capabilities.
Really interesting blog post from the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) on liability and generative AI! Turns out it’s likely going to be difficult to hold model developers liable.
President Biden has issued an Executive Order to lead in AI innovation while addressing safety, privacy, equity, and more. It sets AI safety standards, privacy protection, equitable AI use, and support for consumers and workers. It also promotes innovation and global leadership in AI and emphasizes responsible government AI use.
The issues addressed in this executive order are important. A future cleare legal framework will not only safeguard society, but foster a rapid development of ethical ai.
Chainblx established already some internal guidelines regarding venture investments in AI driven or developing companies. Especially the question of IP and copyright have to be addressed as well
Apropos of AI, a recent article from the CKC.Fund team on the dynamic changes in the digital asset landscape, focusing on the intersection of blockchain technology with real-world assets (RWAs) and artificial intelligence (AI). This article highlights the potential of tokenization to enhance security and authenticity in various assets, facilitating fractionalized investments and increased liquidity. It covers topics such as market capitalization, blockchain adoption, and the projected industry size of tokenized RWAs. Additionally, we examine the potential collaboration between AI and blockchain and delve into the tokenization of assets beyond non-fungible tokens (NFTs).